04 - Exercícios 2
Roads of NITT, Spanning Tree Fraction, Airports
Autor(es):
Explicação dos Exercícios de Grafo
Exercícios B, E e F
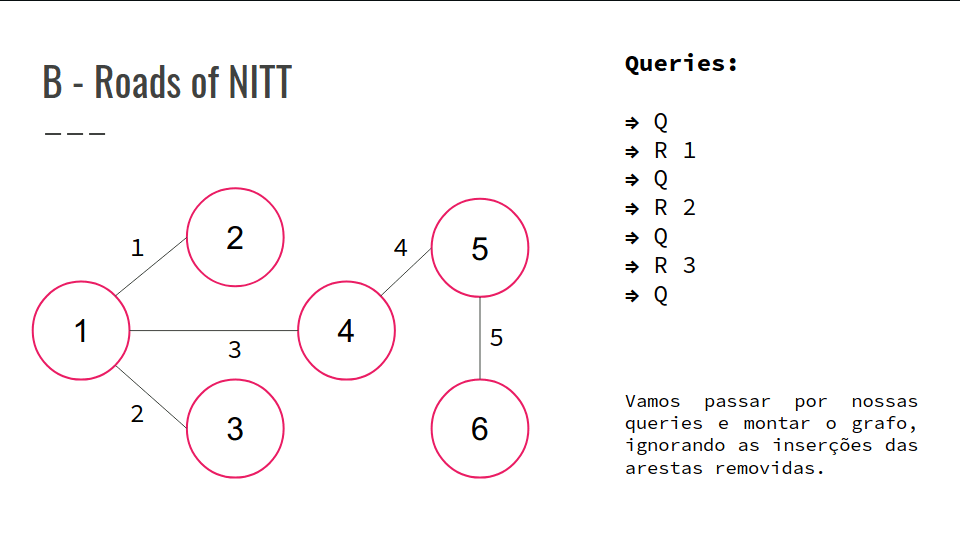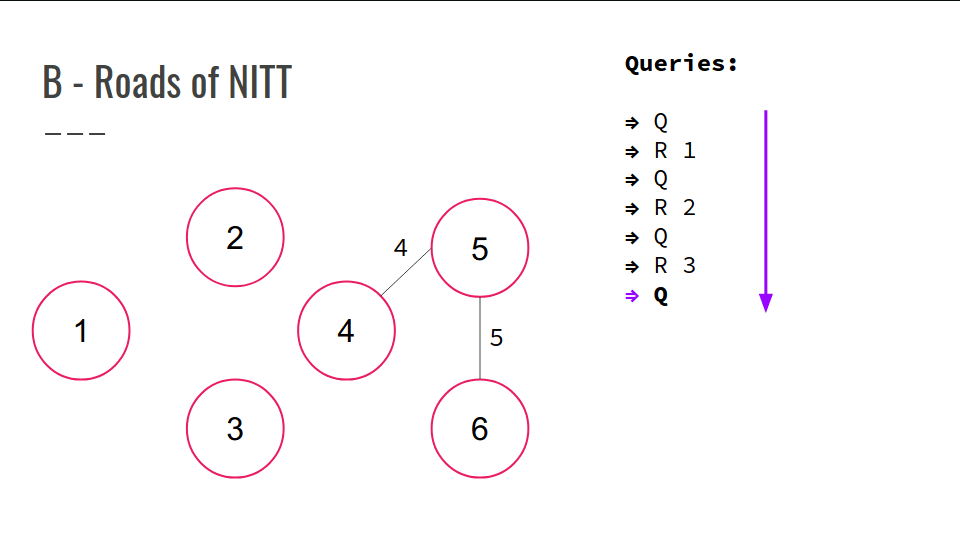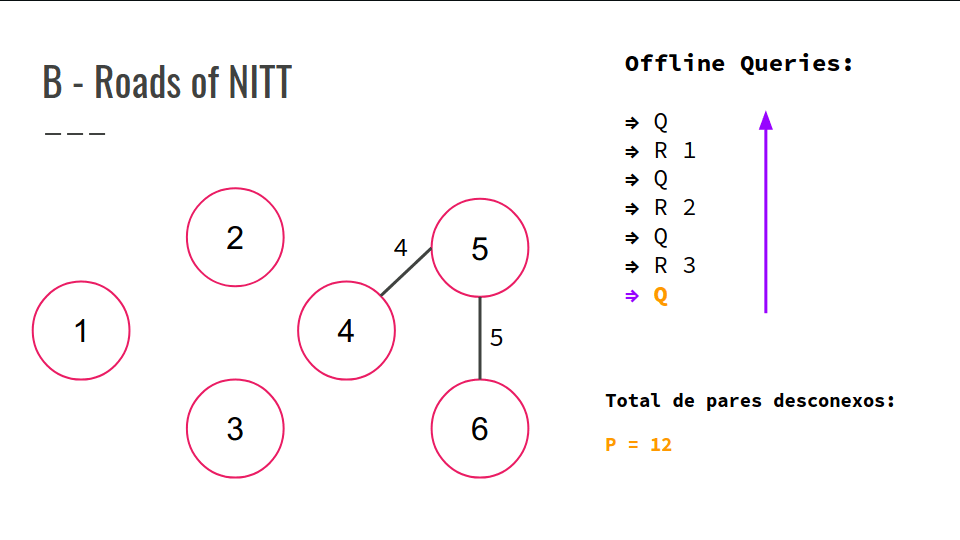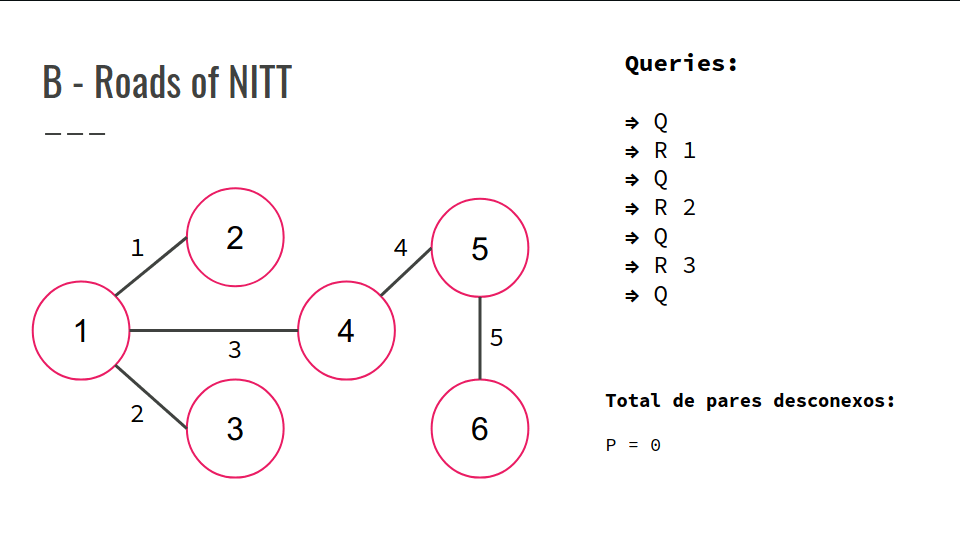
B - Roads of NITT
-
Existem N hotels conectados entre si por N - 1 arestas.
-
No início, sempre existe um caminho entre dois pares de hotéis, mas, com o tempo, algumas rotas se tornam inutilizáveis.
-
Dadas Q consultas, determinar quantos pares de hotéis (X, Y) não tem uma rota entre si.
-
As consultas podem ser de 2 tipos:
- R X -> remove a estrada X. É garantido que ela não foi removida anteriormente.
- Q -> retorna o resultado do número de pares de hotéis (X, Y) que não possuem rota entre si.
-
Confira a GIF abaixo:
ll q;
cin >> q;
vector<bool> used(n);
vi queries(q);
for (ll i = 0; i < q; i++) {
char op;
ll id = -1;
cin >> op;
if (op == 'R') {
cin >> id;
used[id] = true;
}
queries[i] = id;
}
ll conn = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (!used[i]) {
int u, v;
tie(u, v) = edges[i];
u = find(u);
v = find(v);
if (u != v) {
conn += len[u] * len[v];
unite(u, v);
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
find(i);
}
ll tot = n * (n - 1) / 2 - conn;
stack<ll> ans;
for (ll i = q - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ll id = queries[i];
if (id != -1) {
ll u, v;
tie(u, v) = edges[id];
u = find(u);
v = find(v);
if (u != v) {
tot -= len[u] * len[v];
unite(u, v);
}
} else {
ans.push(tot);
}
}
while (!ans.empty()) {
cout << ans.top() << "\n";
ans.pop();
}
cout << "\n";E - Spanning Tree Fraction
- Temos um grafo conexo G com N vértices, indexados de 0 até N - 1, e M arestas.
- Cada aresta desse grafo é uma quádrupla (U, V, a, b), sendo U o vértice de origem, V o vértice de destino, a e b pesos da nossa aresta.
- Achar uma árvore geradora T que contém um subconjunto das M arestas e maximize a expressão ∑i∈T ai / ∑i∈T bi, sendo i o índice da aresta inserida em T.
- Escrever o termo resultante no formato de uma fração irredutível p / q.
bool cmp(tuple<ii, ll, ll> a, tuple<ii, ll, ll> b) {
ii p, q;
p = get<0>(a);
q = get<0>(b);
return (p.first - p.second * x) > (q.first - q.second * x);
}
int main() {
ll n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
parent = len = vi(n + 1);
for (ll i = 0; i < m; i++) {
ll u, v, a, b;
cin >> u >> v >> a >> b;
add_edge(u, v, a, b);
}
ll p, q, gcd;
double left = 0., right = 1e7;
while (fabs(right - left) >= EPSILON) {
x = (left + right) / 2;
for (ll i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
len[i] = 1;
}
p = q = 0;
sort(begin(edges), end(edges), cmp);
kruskal(p, q);
if (p >= q * x) {
left = x;
} else {
right = x;
}
}
gcd = __gcd(p, q);
p /= gcd;
q /= gcd;
cout << p << "/" << q << "\n";
return 0;
}F - Airports
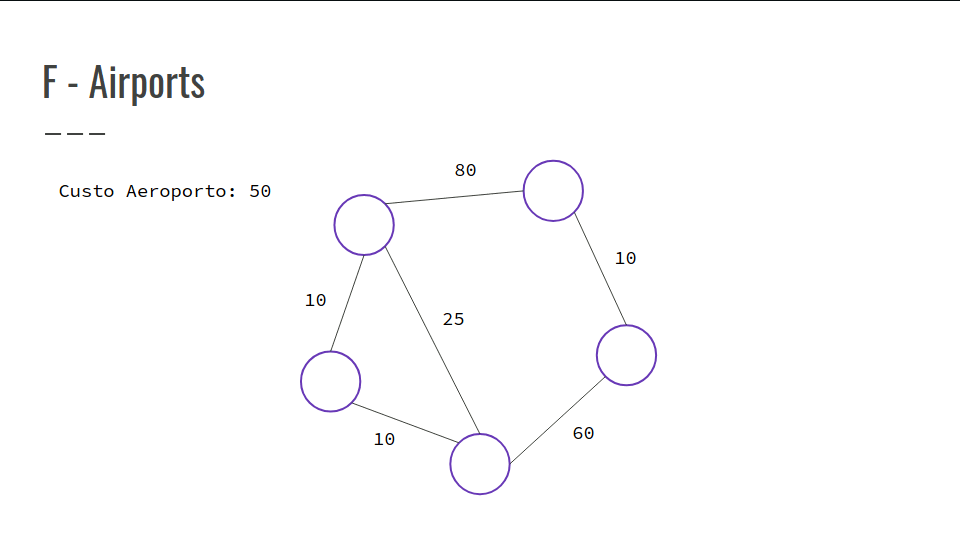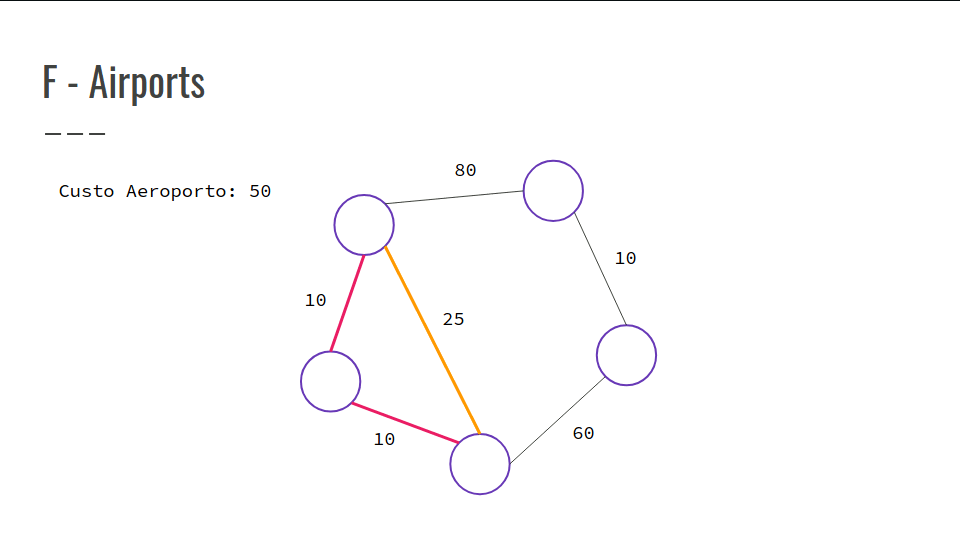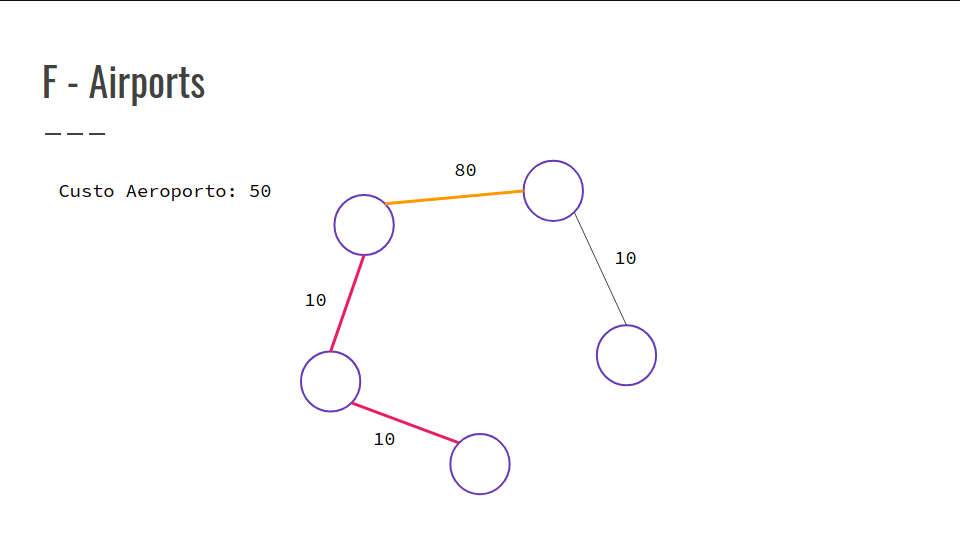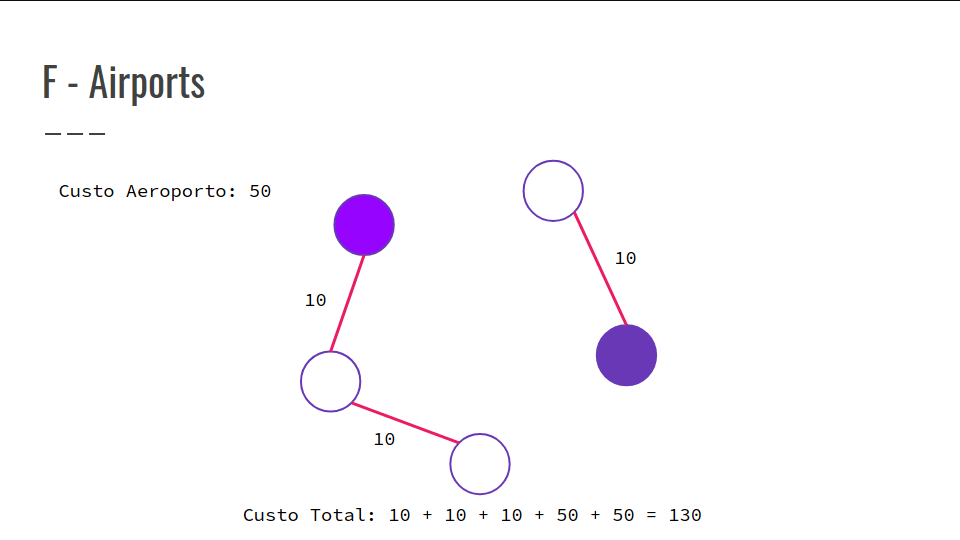
-
Você pode colocar aeroportos em qualquer cidade.
-
São dadas as possíveis pistas que ligam as cidades.
-
Objetivo: Garantir que cada cidade tenha acesso a um aeroporto.
-
Confira a GIF abaixo:
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin >> a >> b >> c;
arestas.push_back({c, a, b});
}
sort(arestas.begin(), arestas.end());
ll custo = 0;
ll ind = lower_bound(arestas.begin(), arestas.end(), make_tuple(aer, 1e17, 1e17))
- arestas.begin();
for(int j = 0; j < ind; j++){
tie(c, a, b) = arestas[j];
if(c == aer)continue;
if(find(a) != find(b)){
merge(a, b);
custo += c;
}
}